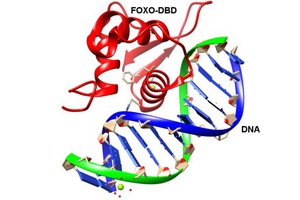
FOXO-DBD
FOXO transcription factors control apoptosis, stress resistance and longevity in mammalian cells. Although the members of the FOXO family act as tumor suppressors in some cell types, emerging evidence suggests ...
We study molecular mechanisms by which protein function can be regulated. In particular, we are interested in 14-3-3 proteins and their complexes with proteins involved in apoptosis, cancer, G-protein and calcium-triggered signaling pathways. We employ both biophysical (fluorescence spectroscopy, analytical ultracentrifugation, SAXS, mass spectrometry, X-ray crystallography, NMR, protein structure modeling, etc.) and biochemical (recombinant protein expression, site-directed mutagenesis) approaches to understand the details of how the activity and function of protein-protein complexes are regulated.
Go to external web page of the group to see more information

FOXO transcription factors control apoptosis, stress resistance and longevity in mammalian cells. Although the members of the FOXO family act as tumor suppressors in some cell types, emerging evidence suggests ...
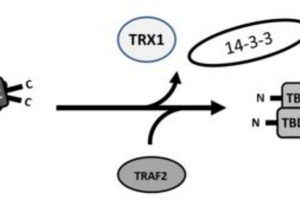
Protein kinase ASK1, a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase family, activates JNK and p38 MAP kinase signaling pathways in response to various stress stimuli, including oxidative stress ...
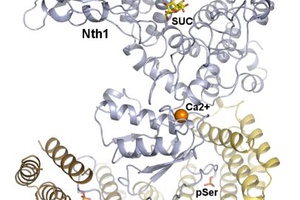
Neutral trehalase 1 (Nth1) catalyses the hydrolysis of trehalose to glucose. Trehalose is found in many organisms ranging from bacteria to higher plants, and in yeast it functions as a ...
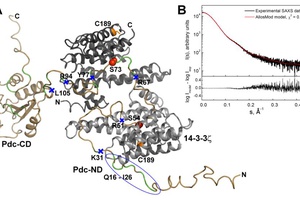
Phosducin (Pdc) is a highly conserved acidic phosphoprotein that regulates visual signal transduction by modulating the
amount of transducin Gtαβγ heterotrimer through competition with the Gta ...

14-3-3 proteins are a family of regulatory molecules, which specifically bind to phosphoserine (or phosphothreonine)- containing motifs (pSer/pThr) in a sequence-specific manner. Through these binding interactions, 14-3-3 proteins play ...